Podiatry
About Our Podiatrist Service At Total Health West Berkshire In Thatcham.
Therapies
Your Feet
Each foot is made up of 26 bones, more than 150 ligaments, an intricate network of muscles, nerves and blood supply – One quarter of all the bones in the human body are in your feet!
The average person will take 10,000 steps per day. Therefore, in a typical lifetime you will walk more than 4 times round the planet (115,000 miles).
75% of all British people will suffer from a foot problem in their lifetime.
Your feet give you: stability and balance; grip and strength to walk and run; shock absorption so that the rest of your body is not jarred as you move
A person weighs more walking than standing. Walking is dead weight plus push energy, which adds about 30% to standing weight, therefore an average male who weighs 70 kgs when standing will weigh 91 kgs when walking, and even more when running!

What We Treat
Importance Of Foot Care
Your feet were made for walking, and it’s important not to tiptoe around the importance of foot health. Despite the distance from your heart, the health of your feet can impact your overall health. It’s important not to ignore foot pain. If your feet hurt, it’s time to see a podiatrist.
The most important reason to take care of your feet is to maintain your quality of life! Your quality of life is directly linked to your ability to be self-sufficient. Activities like working, shopping and walking are just a few of the daily living activities that make you self-sufficient. If you have foot problems or your feet hurt, you won’t be functioning at your best. Even if you have a desk job, you still need to get up occasionally. Poor foot health can not only impede work it can mean you’re less likely to engage in physical activities too, which is detrimental to your overall health!
Who can benefit from seeing a podiatrist
What is the difference between a podiatrist and a foot health practitioner?


Diabetic Foot Care
When you have Diabetes, it can affect your feet, but Why?
Circulation
High blood glucose levels cause fatty deposits to form inside the blood vessels. Over time, these deposits make your blood vessels narrow and harden, reducing the blood flow. The smallest vessels are affected first, most commonly, in the eyes, kidneys and the feet.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a condition often seen in conjunction with diabetes, and is where fatty deposits attach to the blood vessels in the legs, this can be caused by atherosclerosis. Risk factors for PAD are smoking, high blood pressure and high cholesterol. It is estimated that ⅓ of people over 50 with diabetes, also have PAD.
Neuropathy is one of the long-term complications of diabetes. Over time, high blood glucose levels can damage the small blood vessels which supply the nerves with nutrients. As a result, the nerve fibres can become damaged and can disappear. Damaged nerves can cause symptoms like numbness, pins & needles, coldness and even pain as the nerves malfunction.
Nerve problems can start in the first 10 years after being diagnosed, with the risk increasing annually and with unstable blood glucose management. It is estimated that ½ of people with diabetes have some form of neuropathy.
As a consequence of the reduced blood flow and damage to the nerves, the skin can become dryer – this is due to the nerves affecting the body’s ability to control oil and moisture levels in the foot, leading to the risk of the skin cracking and fissures appearing on the heels.
Hard skin (callus) can also build up faster on people with diabetes where there are high pressure areas, such as the ball of the foot, the heel and the big toe.
The increased levels of glucose in the blood also reduces the nutrients and oxygen from reaching the blood cells, prevents the immune system from functioning effectively and delays the speed of healing of the skin.
The longer the skin is broken, the higher the risk of an infection entering the tissue, and once inside, the higher than normal blood sugar levels increase the chance of the infection as bacteria thrive on a high sugar diet.
Your Podiatrist will regularly test your blood flow by listening to your pulses, and check your nerve sensations at your annual assessment, depending on the results, your feet will have a low, increased or high risk of developing an ulcer.
This is why you should see your Podiatrist at least once a year to have your “Foot Risk” assessed.
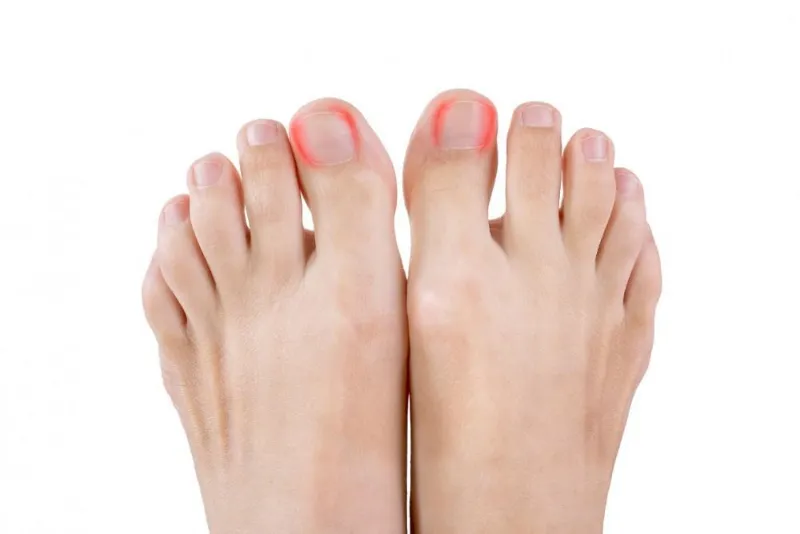
Ingrown toenails
What is an ingrown toenail?
An ingrowing toenail develops when the sides of the toenail grow into the surrounding skin. The nail curls and pierces the skin, which becomes red, swollen, and tender which can become infected.
The big toe is often affected, either on one or both sides. Other possible symptoms include:
- Pain if pressure is placed on the toe
- Inflammation of the skin at the end of the toe
- A build-up of fluid in the area surrounding the toe
- An overgrowth of skin around the affected toe
- Bleeding
- White or yellow pus coming from the affected area
- What causes an ingrown toenail?

A number of things can cause an ingrown toenail to develop, including:
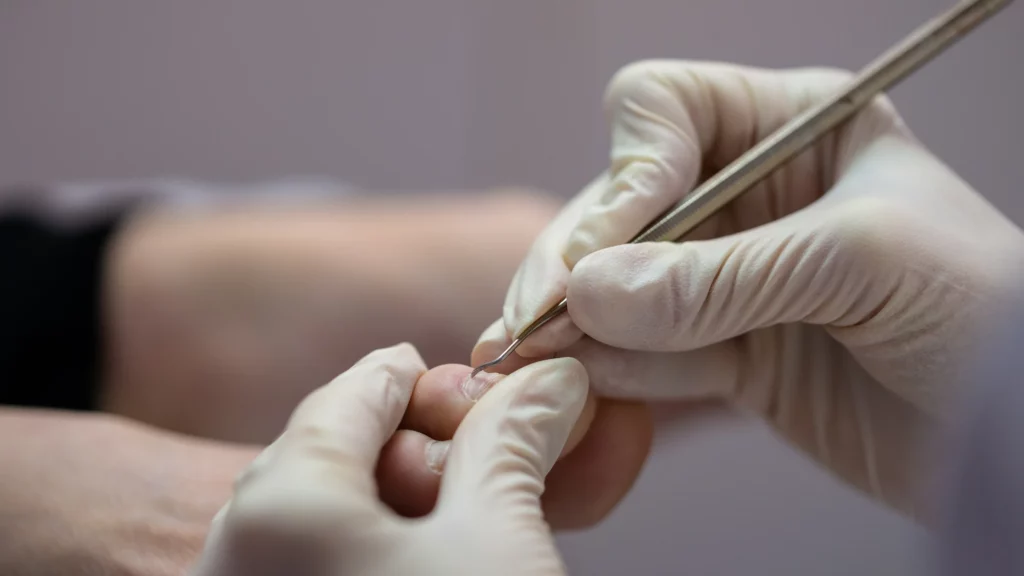
What does the Procedure Involve?
To begin, the toe is made completely numb with a local anaesthetic, when the toe is completely numb (and we always check!), an antiseptic solution will be applied to your toe to minimise the chance of infection. The offending nail or piece of the nail will then be removed.
A chemical solution (phenol) is then applied to stop the nail from regrowing.
A protective dressing will be applied, and the operation is complete. The whole procedure is over and done within 45 minutes-1 hour (for 1 toe).
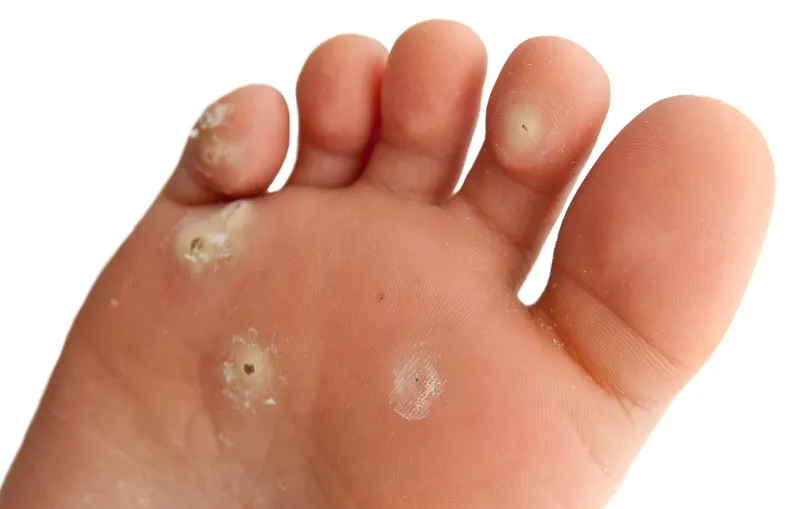
What is a Verruca?
A Verrucae (or plantar wart) is usually found on the bottom of the foot and is a small skin lesion usually around 1cm in diameter, but they can grow bigger.
Usually associated with children, verrucae are also a common complaint amongst adults.
All verrucae are caused by the human papilloma virus which is common in all environments but does not readily attack the skin. Due to this though verrucae are commonly contracted in communal places such as swimming pools, showers and changing areas, this is why children are more at risk of contracting verrucae in school changing rooms and swimming pools.
If there is excessive moisture or excessive dryness of the skin this can lead to small cracks in the skin which allows the virus to enter
What are the treatment options?
Verrucae can be removed with over-the-counter treatments, but these don’t always work. The treatments include things like creams, gels, skin paints and medicated plasters which contain salicylic acid, the salicylic acid is used to burn the top layer of the affected skin. You can also find cold sprays that contain dimethyl ether propane, these sprays are used to freeze the wart. Other topical treatments which can be applied by a Podiatrist, along with Falknor’s Needling and Swift are other available treatments.
Here at Total Health West Berkshire we offer Swift treatment for verrucas.
Swift uses microwave energy to attack infected areas of the skin and stimulate healing. The treatment works by applying bursts of localised microwave energy to the infected skin through a special handheld probe. You can find more information about our Swift treatment here.
Fungal Nails & Skin
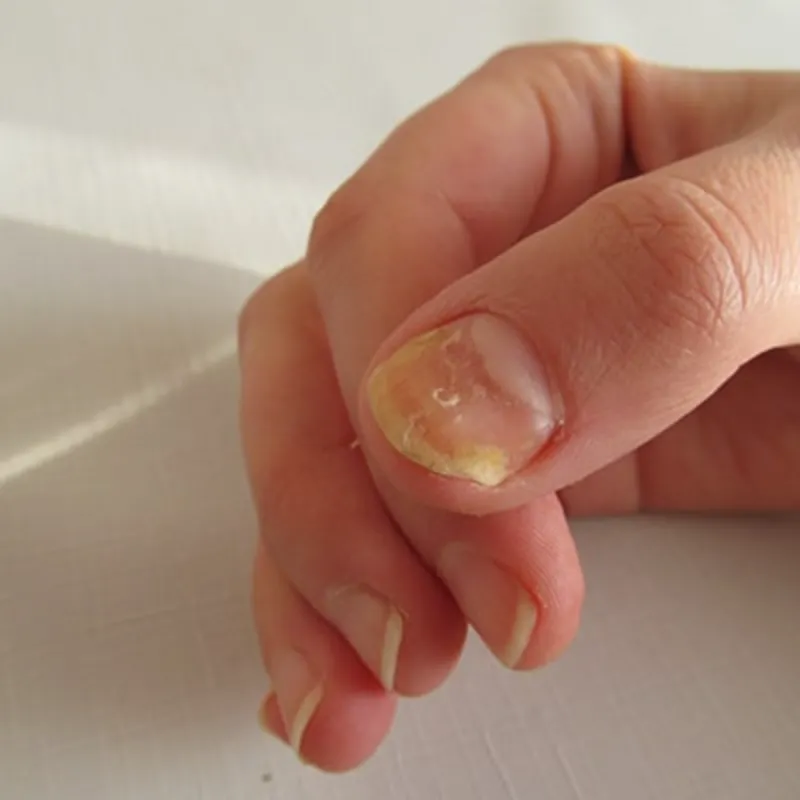
What are Fungal Nails?
Fungal nail infections (onychomycosis) are common and can affect both the fingernails and the toenails. The problem usually affects more men than women and becomes more common the older you become.
A fungal nail infection causes visual changes to the nail. It causes the nail to change colour, thicken and become brittle. As the infection progresses the nails will start to produce a distinct odour.
Around half of all nail problems are due to fungal nail infections.
Fungi called Dermatophytes live harmlessly on the skin but can often multiply and lead to infection in dark, warm and moist environments such as the feet. Certain shoes can cause the feet to become hot and sweaty which can lead the fungi to multiply quickly. Not keeping the feet clean and dry can also speed up the infection risk.
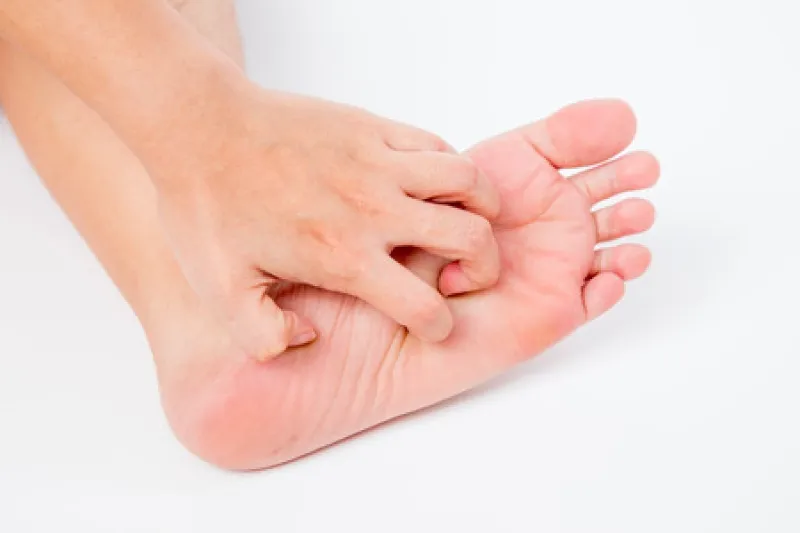
What is Athlete’s Foot?
Athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) is a common fungal skin infection commonly found between the toes and on the sole of the foot. The skin becomes itchy which can cause real discomfort.
Athlete’s foot can cause the skin to flake and peel. As the skin is itchy you are more likely to scratch which can cause the skin to split. In severe cases a secondary infection can occur where the skin has split.
Fungal infections thrive in dark, warm and moist environments. Inside the shoe is the perfect environment for an infection to develop.
Athlete’s foot can be spread by direct contact or by touching a surface that has been in contact with the infected area.
Gyms and changing rooms are often cited as places for the infection to spread due to the warm moist environment.
How do they work?
Team



